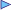
| 字 | 部首 | 異體字 | 讀音 | 今譯 | 漢語詞典 | 康熙字典 | 辭海 |
|---|
| 君 | 口+4 | 𠱩 𠱭 | jūn ㄐㄩㄣ | 天子。 / 國君。 / 大夫。 / 為君。 / 統治、治理。 | 卷1頁0595第06 | 頁177第07 | 卷2頁5660第8 |
| 舉 | 臼+10 | 擧 㪯 举 | jǔ ㄐㄩˇ | raise, lift up; recommend | 卷5頁3041第08 | 頁1005第15 | 卷1頁1143第01 |
| 旅 | 方+6 | 旅 𣥏 𣃨 魯 𣥐 | lǚ ㄌㄩˇ | trip, journey; travel; traveler | 卷3頁2178第07 | 頁483第02 | 卷6頁2360第2 |
| 於 | 方+4 | 烏 𣱏 𤕘 于 亏 扵 | yú ㄩˊ | 為,作。 / 在,存在。 / 介詞,相當於「在」。 / 介詞,相當於「從」、「到」。 / 介詞,相當於「比」。 / 介詞,相當於「給」、「對」、「向」。 / 介詞,相當於「被」。 / 介詞,相當於「以」、「用」。 / 介詞,相當於「由於」、「在於」。 / 介詞,相當於「依據」、「按照」。 / 連詞,相當於「猶與」、「而」。 / 助詞,無義。 | 卷3頁2175第02 | 頁481第11 | 卷6頁2220第3 |
| 賓 | 貝+7 | 𧶉 𡫅 𥦎 𡧍 賔 宾 | bīn bìn ㄅㄧㄣ ㄅㄧㄣˋ | guest, visitor; surname; submit | 卷6頁3643第08 | 頁1208第37 | 卷1頁2755第05 |
| 及 | 又+2 | 𢎜 𨕤 | jí ㄐㄧˊ | 追及,趕上。 / 挽回。 / 做得到,趕得上,比得上。 / 至,到。 / 觸及。 / 涉及,推及。 / 繼。 / 介詞:表示動作的時間:趁著、等到...時間。 / 連詞:表示並列,相當於「和」。 | 卷1頁0035第01 | 頁165第03 | 卷2頁3340第6 |
| 所 | 戶+4 | 𢨷 | suǒ ㄙㄨㄛˇ | 處所,地方。 / 位置。 / 適宜、適當的處所或位置。 / 量詞:多用來計算建築物。 / 用在動詞之前,構成名詞性的詞組,指代人或事物。 / 如,若。多用在誓詞或咒語中,表示假設。 / 和「為」字配合使用,表示被動。 / 約略估計之數,相當於「許」。 / 數,次數。 / 意態,意思。 | 卷3頁2259第01 | 頁415第16 | 卷5頁5610第1 |
| 賜 | 貝+8 | 赐 | cì ㄘˋ | 賞給。 / 賜予的恩惠或財物。 / 盡。 | 卷6頁3648第02 | 頁1209第15 | 卷1頁2763第04 |
| 爵 | 爪+14 | 𥥼 𩰧 𣡫 𠙘 | jué ㄐㄩㄝˊ | feudal title or rank | 卷3頁2037第06 | 頁689第29 | |
| 皆 | 白+4 | | jiē ㄐㄧㄝ | all, every, everybody | 卷4頁2647第01 | 頁786第12 | 卷7頁3550第1 |
| 降 | 阜+6 | 降 夅 | jiàng xiáng xiàng ㄐㄧㄤˋ ㄒㄧㄤˊ ㄒㄧㄤˋ | descend, fall, drop; lower, down | 卷6頁4126第18 | 頁1349第12 | 卷1頁4212第02 |
| 再 | 冂+4 | | zài ㄗㄞˋ | again, twice, re- | 卷1頁0018第01 | 頁129第08 | 卷1頁6450第5 |
| 拜 | 手+5 | 拝 𣬊 𣬓 𢰛 𢴽 𡴬 | bài ㄅㄞˋ | do obeisance, bow, kowtow | 卷3頁1846第07 | 頁427第02 | 卷5頁7140第1 |
| 稽 | 禾+10 | 乩 𩠜 | jī qǐ ㄐㄧ ㄑㄧˇ | examine, investigate; delay | 卷4頁2622第08 | 頁858第01 | 卷9頁9450第3 |
| 首 | 首+0 | 𩠐 𥃻 | shǒu ㄕㄡˇ | head; first; leader, chief; a poem | 卷7頁4500第01 | 頁1427第32 | 卷1頁4952第04 |
| 升 | 十+2 | 昇 | shēng ㄕㄥ | 容量單位,一斗的十分之一。 / 量酒單位。 / 古代布八十縷為一升。 / 登上,上升。 / 成熟。 / 進奉,進獻。 | 卷1頁0033第05 | 頁156第03 | 卷2頁1410第3 |
| 成 | 戈+2 | 𢦩 | chéng ㄔㄥˊ | completed, finished, fixed | 卷2頁1399第01 | 頁411第11 | |
| 明 | 日+4 | 朙 | míng ㄇㄧㄥˊ | 明亮,光明。 / 白天。 / 顯明,清楚。 / 明確,闡明。 / 明白,懂得。 / 明白地。 / 明淨,淨潔。 / 明智,賢明。 / 使明智。 / 神靈,神明。 / 敬。 / 視力。 / 視力好。 / 看得清楚。 / 今之次。第二(天、月、年)。 | 卷2頁1491第08 | 頁491第12 | 卷6頁3130第1 |
| 臣 | 臣+0 | 𢘑 | chén ㄔㄣˊ | minister, statesman, official | 卷4頁2801第01 | 頁999第13 | 卷1頁1062第02 |
| 禮 | 示+13 | 禮 礼 𠃞 𤔑 礼 | lǐ ㄌㄧˇ | social custom; manners; courtesy; rites | 卷4頁2409第14 | 頁847第07 | 卷9頁8520第4 |
| 也 | 乙+2 | 𠃟 匜 | yě ㄧㄝˇ | 句末語氣詞:表示判斷和肯定。 / 句末語氣詞:用在疑問句尾加強疑問語氣。 / 句末語氣詞:用在因果句尾表示解釋。 / 句中語氣詞:表示語氣的停頓。 | 卷1頁0050第05 | 頁84第04 | 卷5頁5101第 |
| 答 | 竹+6 | 荅 畣 畗 | dá dā ㄉㄚˊ ㄉㄚ | answer, reply; return; assent to | 卷5頁2968第01 | 頁883第13 | 卷1頁0135第02 |
| 之 | 丿+3 | 㞢 | zhī ㄓ | 往,到......去。 / 指示代詞:這。 / 第三人稱代詞:他、她、它。 / 助詞:相當於「的」。 / 助詞:用於主語和謂語之間,取消句子的獨立性。 / 助詞:在句中只起調節音節的作用,無實義。 | 卷1頁0043第01 | 頁82第04 | 卷4頁7202第 |
| 無 | 火+8 | 𣟒 𣚨 𠘩 无 橆 | wú ㄨˊ | 沒有。 / 古代哲學範疇,指虛無、空虛等。 / 副詞:表示否定,相當於「不」、「未」。 / 副詞:表示疑問,相當於「否」。 / 連詞:表示條件關係,相當於「無論」、「不論」。 / 連詞:表示假設關係,相當於「即使」。 / 助詞:用於句首,無實義。 / 通「勿」、「毋」:表示禁止,相當於「不要」、「別」。 / 通「蕪」:荒蕪。 | 卷3頁2211第15 | 頁673第26 | 卷8頁4820第4 |
| 不 | 一+3 | 不 𠀚 𠙐 | bù ㄅㄨˋ | 無,沒有。 / 非,不是。 / 否定副詞:用於動詞、形容詞等前面,表示否定。 / 否定副詞:表示禁止,相當於「勿」、「不要」。 / 否定副詞:表示反問,常與「乎」相呼應。 | 卷1頁0011第06 | 頁76第15 | 卷3頁0101第 |
| | | | fǒu ㄈㄡˇ | 通「」 fǒu ㄈㄡˇ: 副詞:和肯定詞對用時,表示否定的一面。 / 通「」 fǒu ㄈㄡˇ: 副詞:用於疑問句末,構成是非問句。 | | | |
| | | | fū ㄈㄨ | 通「柎」,花萼。 | | | |
| | | | pī ㄆㄧ | 通「」 pī ㄆㄧ: 大。 | | | |
| | | | bǐ ㄅㄧˇ | 通「鄙」:鄙視,不敬重。 | | | |
| 上 | 一+2 | 丄 𠄞 | shàng ㄕㄤˋ | top; superior, highest; go up, send up | 卷1頁0005第04 | 頁76第07 | 卷2頁4201第 |
| 下 | 一+2 | 丅 厥 𠄟 | xià ㄒㄧㄚˋ | under, underneath, below; down; inferior; bring down | 卷1頁0007第01 | 頁76第10 | 卷2頁8101第 |
| 竭 | 立+9 | | jié ㄐㄧㄝˊ | put forth great effort; exhaust | 卷4頁2713第20 | 頁872第29 | 卷1頁0053第04 |
| 力 | 力+0 | 力 𠠲 | lì ㄌㄧˋ | power, capability, influence | 卷1頁0364第04 | 頁146第05 | 卷1頁9140第3 |
| 盡 | 皿+9 | 𥁞 尽 | jìn ㄐㄧㄣˋ | 完,沒有了。 / 終止,完結。 / 死。 / 到...為止。 / 竭盡,盡力表現出某種動作行為。 / 窮盡。 / 事物達到的極限或頂點。 / 話說得明白,透徹。 / 全,全部。 / 極,最。 / 通「進」:前進。 / 通「贐」:費用。 | 卷4頁2567第05 | 頁795第22 | 卷9頁4030第5 |
| 能 | 肉+6 | | néng ㄋㄥˊ | 獸名。 / 才能。 / 有才能的人。 / 能夠,勝任。 / 順從,親善。 / 容,得。 / 及,到。 / 乃,就。 / 通「」 ér ㄦˊ: 連詞:表示假設,相當於「如果」。 / 只,僅。 / 寧,寧可。 / 恁,這樣,如此。 / 三足鱉。 | 卷3頁2074第01 | 頁981第16 | 卷1頁0955第02 |
| | | | nài ㄋㄞˋ | 通「耐」:受得住。 | | | |
| | | | tái ㄊㄞˊ | 通「」 tái ㄊㄞˊ: 星名,即三台。 見「三能」。 | | | |
| | | | tài ㄊㄞˋ | 通「態」:形態。 | | | |
| 以 | 人+3 | 㠯 | yǐ ㄧˇ | 用,使用。 / 認爲。 / 率領。 / 帶。 / 連及。 / 有。 / 原因。 / 介詞:因爲。 / 介詞:從,在。 / 介詞:在...時候。 / 介詞:拿,用。 / 介詞:按照,依照。 / 介詞:依靠。 / 介詞:憑藉...身份。 / 介詞:跟,同。 / 連詞:表示後一行動是前一行動的目的。 / 連詞:用在狀語與動詞之間,表示修飾。 / 連詞:表示並列,有「並且」的意思。 / 連詞:表示轉折,有「但是」的意思。 / 連詞:表示結果,有「因而」的意思。 / 助詞:和某些方位詞、時間詞等連用,表示時間和方位。 / 句末、句中語氣詞。 / 通「」 yǐ ㄧˇ: 停止,廢止。 / 通「」 yǐ ㄧˇ: 副詞:已經。 / 通「」 yǐ ㄧˇ: 副詞:甚,太。 | 卷1頁0105第07 | 頁94第01 | 卷8頁7601第 |
| 立 | 立+0 | 立 | lì ㄌㄧˋ | 站立,站著。 / 豎立。 / 建立,設置。 / 制定,訂立。 / 決定,確立。 / 立身,自立。 / 存在,生存。 / 出仕,任職。 / 君王登位,即位。 / 停止,停留。 / 立即,立刻。 | 卷4頁2706第01 | 頁870第17 | 卷1頁0025第01 |
| 功 | 力+3 | | gōng ㄍㄨㄥ | achievement, merit, good result | 卷1頁0365第08 | 頁146第11 | 卷1頁9230第3 |
| 國 | 囗+8 | 圀 國 囗 囶 𢧌 䆐 囯 国 | guó ㄍㄨㄛˊ | nation, country, nation-state | 卷1頁0720第09 | 頁219第16 | 卷3頁0340第2 |
| 必 | 心+1 | | bì ㄅㄧˋ | surely, most certainly; must | 卷4頁2267第02 | 頁375第02 | 卷5頁2250第1 |
| 報 | 土+9 | 报 | bào ㄅㄠˋ | report, tell, announce | 卷1頁0466第04 | 頁234第05 | 卷3頁2440第1 |
| 祿 | 示+8 | 祿 禄 | lù ㄌㄨˋ | blessing, happiness, prosperity | 卷4頁2402第08 | 頁844第08 | 卷9頁8240第4 |
| 故 | 攴+5 | | gù ㄍㄨˋ | 緣故,原因。 / 事。 / 變故,事故。 / 計謀,巧僞。 / 舊,與「新」相對。 / 從前,原來的。 / 死亡。 / 故意 / 固、本來。 / 連詞:所以,因此。 | 卷2頁1453第05 | 頁469第25 | 卷6頁0150第1 |
| 務 | 力+9 | 务 | wù ㄨˋ | 致力,專力從事。 / 追求,謀求。 / 事、事情。 / 務必,一定。 | 卷4頁2765第09 | 頁148第20 | 卷1頁9750第1 |
| | | | wǔ ㄨˇ | 通「侮」:欺侮。 | | | |
| | | | mào ㄇㄠˋ | 通「暓」:亂,眩惑。 | | | |
| 是 | 日+5 | 昰 𣆞 | shì ㄕˋ | 直,正。 / 正確。 / 認爲正確,肯定。 / 指示代詞:此。 / 判斷詞。 / 助詞,用於前置賓語之後。 | 卷2頁1497第05 | 頁493第26 | 卷6頁3910第1 |
| 安 | 宀+3 | | ān ㄢ | 安穩,穩定。 / 安定,平靜。 / 安全。 / 安於,習慣於。 / 安心。 / 安適,安逸。 / 止息,停止。 / 徐緩,從容。 / 安放,安置。 / 疑問代詞:如何,怎麼。 / 疑問代詞:哪裡。 / 疑問代詞:什麼。 / 疑問代詞:誰,什麼人。 / 連詞:乃,於是。 | 卷2頁0913第09 | 頁282第08 | 卷4頁0620第1 |
| 而 | 而+0 | | ér ㄦˊ | 頰毛。 / 如,像,似。 / 代詞:你,你們。 / 代詞:此,這樣。 / 連詞:表示並列,相當於「和」、「與」。 / 連詞:表示順承,相當於「就」、「才」。 / 連詞:表示假設,相當於「如果」。 / 連詞:表示轉折,相當於「卻」、「但是」。 / 連詞:表示因果,相當於「因而」、「所以」。 / 連詞:表示方式或狀態。 / 助詞:相當於「之」。 / 助詞:表示語氣,相當於「啊」或「吧」。 | 卷4頁2810第01 | 頁961第18 | 卷1頁0802第03 |
| | | | néng ㄋㄥˊ | 通「」 néng ㄋㄥˊ: 能夠,勝任。 / 通「」 néng ㄋㄥˊ: 才能。 | | | |
| 寧 | 宀+11 | 寍 𡨴 宁 | níng nìng zhù ㄋㄧㄥˊ ㄋㄧㄥˋ ㄓㄨˋ | repose, serenity, peace; peaceful | 卷2頁0949第05 | 頁291第08 | 卷4頁2860第1 |
| 言 | 言+0 | 訁 𢍗 𢍬 | yán ㄧㄢˊ | 説話,說。 / 談論,議論。 / 告訴。 / 言論,學説。 / 一個字為一言。 / 一句話為一言。 / 助詞,無實義。 | 卷6頁3936第01 | 頁1146第01 | 卷1頁2365第03 |
| 虛 | 虍+6 | 𣦄 虚 | xū ㄒㄩ | false, worthless; empty, hollow | 卷4頁2825第06 | 頁1074第11 | 卷1頁1841第06 |
| 取 | 又+6 | | qǔ ㄑㄩˇ | 割下(耳朵)。 / 捕捉,俘獲。 / 拿,索取。 / 獲得。 / 招致。 / 輕易征服城邑和戰敗敵軍。 / 戰勝,奪取。 / 提取。 / 採取,擇取。 / 選拔,錄用。 / 娶。 / 副詞:表示範圍。僅僅。 | 卷1頁0395第01 | 頁166第04 | 卷2頁3630第1 |
| 正 | 止+1 | 㱏 𣥔 𤴓 𧾸 | zhèng ㄓㄥˋ | 不偏,不斜。 / 正當,合適。 / 正常。 / 正派,正直。 / 正定,確定。 / 整治,治理。 / 治罪。 / 正式的,為主的。與「副」相對。 / 純正,正宗。 / 嫡長。與「庶」相對。 / 恰好,正好。 / 表示動作或狀態的進行和持續。 / 官長。 / 只。 / 通「政」:政治,政事。 / 通「證」:證明,驗證。 | 卷2頁1436第01 | 頁574第02 | 卷7頁3250第2 |
| | | | zhēng ㄓㄥ | 陰曆每年的第一個月。見「正月」。 / 箭靶中心。 / 通「征」:征伐。 | | | |
| 道 | 辵+9 | 𨕥 衟 𡬹 | dào ㄉㄠˋ | 路,道路。 / 路程。 / 途徑,方法。 / 規律,道理。 / 學説,主張。 / 技藝。 / 道義,正道。 / 道家所說的萬物之源。 / 說,談論。 / 取道,行。 / 從,由。 / 祭祀路神。 / 古代行政區劃名。 / 指道家或道教。 | 卷6頁3864第01 | 頁1262第06 | 卷1頁3263第02 |
| | | | dǎo ㄉㄠˇ | 引導。(後作「導」) / 疏通。(後作「導」) | | | |
| 民 | 氏+1 | 𠘽 | mín ㄇㄧㄣˊ | people, subjects, citizens | 卷3頁2131第01 | 頁598第01 | 卷7頁5030第1 |
| 有 | 月+2 | | yǒu ㄧㄡˇ | 有。與「無」相對,表示領有。 / 藏有。 / 占有。 / 保有。 / 富有。 / 豐收。 / 得有。 / 只有。 / 有。與「無」相對,表示存在。 / 發生。 / 為。 / 助詞:放在名詞前,無實義。 / 助詞:放在單音形容詞前,無實義。 / 助詞:放在動詞前,無實義。 / 尚,仍。 / 有的人。 / 通「域」:地域,州域。 | 卷3頁2041第05 | 頁504第20 | 卷6頁5650第1 |
| | | | yòu ㄧㄡˋ | 通「佑」:幫助。 / 通「」 yòu ㄧㄡˋ: 又:表示意思更進一層。 | | | |
| 然 | 火+8 | 燃 𤓉 | rán ㄖㄢˊ | 「燃」的本字:燃燒。 / 指示代詞:如此,這樣,那樣。 / 表示肯定,相當於「對」、「是」。 / 認爲對的。 / 副詞:竟,便。 / 連詞:表示轉折,相當於「可是」、「但」、「卻」。 / 助詞:用於句尾,表示比擬。相當於「...一般」、「...似的」。 / 助詞:用於形容詞、副詞之後,表示狀態。 / 助詞:用於句尾,表示肯定語氣,相當於「焉」。 | 卷3頁2213第05 | 頁675第12 | 卷8頁5250第1 |
| 後 | 彳+6 | 𨒥 𢔏 后 | hòu ㄏㄡˋ | 位置在後,與「前」相對。 / 落在後面。 / 時間較晚,與「先」、「前」相對。 / 將來,未來。 / 後代,子孫。 | 卷2頁0822第03 | 頁366第18 | 卷5頁1120第1 |
| 其 | 八+6 | 丌 亓 | qí ㄑㄧˊ | 代詞:表示第三人領屬關係,相當於「他的」、「它的」等。 / 指示代詞,相當於「那」、「那些」。 / 副詞:表示推測、估計,相當於「大概」、「或許」。 / 副詞:表示祈使,相當於「可要」、「當」。 / 副詞:表示反詰,相當於「豈」、「難道」。 / 副詞:表示未來時,相當於「將」。 / 連詞:表示假設,相當於「如果」。 / 連詞:表示選擇,相當於「或者」、「還是」。 / 連詞:表示讓步,相當於「尚且」。 / 助詞:在形容詞之後,相當於「然」。 / 助詞:在偏正短語之間,相當於「之」。 / 助詞:在單音節形容詞(或象聲詞)之前,起加強形容、狀態的作用。 / 助詞:在句中,無實義,起調整音節的作用。 | 卷1頁0245第01 | 頁127第18 | 卷1頁6250第1 |
| | | | jì ㄐㄧˋ | 助詞:常附在「彼」、「何」之後。 | | | |
| | | | jī ㄐㄧ | 語氣詞:表示疑問語氣。 / 「朞」的古字:周年。 | | | |
| 什 | 人+2 | 什 | shí shén ㄕˊ ㄕㄣˊ | file of ten soldiers; mixed, miscellaneous | 卷1頁0108第02 | 頁91第06 | 卷8頁2602第 |
| 一 | 一+0 | 弌 壹 | yī ㄧ | one; a, an; alone | 卷1頁0001第01 | 頁75第01 | 卷1頁101第 |
| 用 | 用+0 | 𤰆 𠛁 | yòng ㄩㄥˋ | use, employ, apply, operate; use | 卷1頁0097第05 | 頁755第24 | 卷9頁0860第2 |
| 足 | 足+0 | 疋 𤴕 | zú jù ㄗㄨˊ ㄐㄩˋ | foot; attain, satisfy, enough | 卷6頁3686第01 | 頁1221第17 | 卷1頁2876第03 |
| 匱 | 匚+12 | 樻 鐀 櫃 饋 匮 | guì kuì ㄍㄨㄟˋ ㄎㄨㄟˋ | to lack | 卷1頁0089第14 | 頁154第20 | 卷2頁0650第2 |
| 和 | 口+5 | 龢 咊 惒 | hé huò huó hè ㄏㄜˊ ㄏㄨㄛˋ ㄏㄨㄛˊ ㄏㄜˋ | harmony, peace; peaceful, calm | 卷1頁0602第01 | 頁185第01 | 卷2頁6730第1 |
| 親 | 見+9 | 𢈥 寴 𡩁 亲 | qīn ㄑㄧㄣ | 父母。 / 親戚,親人。 / 愛,寵愛。 / 近,親密。 / 接觸。 / 親自。 / 躬親,親自治理。 | 卷6頁3671第12 | 頁1136第12 | 卷1頁2305第04 |
| 相 | 目+4 | | xiāng ㄒㄧㄤ | 互相,交互。 / 先後,遞相。 / 共同,一起。 | 卷4頁2470第13 | 頁800第18 | 卷9頁4510第1 |
| | | | xiàng ㄒㄧㄤˋ | 觀察,看。 / 相貌。 / 看相,通過察看人的相貌推測其命運。 / 幫助,輔佐。 / 盲人的向導。 / 宰相,丞相。 / 贊禮官,司儀。 | | | |
| 怨 | 心+5 | 𢘖 𠨝 𢛪 𢘔 𢘈 | yuàn ㄩㄢˋ | hatred, enmity, resentment | 卷4頁2281第07 | 頁382第01 | 卷5頁2740第1 |
| 此 | 止+2 | | cǐ ㄘˇ | 這。與「彼」相對。 / 這般,這樣。 / 這裡。 / 副詞:猶「乃」、「則」。 | 卷2頁1438第03 | 頁574第10 | 卷7頁3540第1 |
| 大 | 大+0 | 𠘲 | dà ㄉㄚˋ | 與「小」相對。 / 大於,超過。 / 以...為大,尊崇。 / 多。 / 粗,厚。 / 年長。 / 敬辭:如「大人」、「大王」等。 / 副詞:表示程度高或範圍廣。 | 卷1頁0520第01 | 頁248第01 | 卷3頁4230第3 |
| | | | tài ㄊㄞˋ | 通「太」:最。 / 通「太」:過分。 / 通「泰」:安定。 | | | |
| 義 | 羊+7 | 义 | yì ㄧˋ | right conduct, righteousness | 卷5頁3133第02 | 頁952第32 | 卷1頁0713第01 |
| 故 | 攴+5 | | gù ㄍㄨˋ | (8) 連詞:所以,因此。 Hence, thus. | 卷2頁1453第05 | 頁469第25 | 卷6頁0150第1 |
| 曰 | 曰+0 | | yuē ㄩㄝ | 說。 / 稱,叫做。 / 助詞。 | 卷2頁1482第02 | 頁502第01 | 卷6頁4830第3 |
| 燕 | 火+12 | 鷰 | yàn yān ㄧㄢˋ ㄧㄢ | swallow (bird); comfort, enjoy | 卷3頁2239第06 | 頁683第16 | 卷8頁5920第1 |
| 者 | 老+4 | | zhě ㄓㄜˇ | 代詞:用於動詞、形容詞等詞語之後,指人或事物。 / 代詞:用於數字之後,指代事物。 / 代詞:用於時間詞或否定詞之後,表示「...時候」或「...的話」。 / 語氣詞:用於判斷句,放在主語之後,引出判斷。 / 語氣詞:用於主語之後,引出原因、解釋等。 | 卷4頁2780第05 | 頁961第01 | 卷1頁0801第01 |
| | | | zhuó ㄓㄨㄛˊ | 通「著」:居、處於。 | | | |